സിവില് സര്വ്വീസ് പരീക്ഷ: 'നേരിട്ടുള്ള ജനാധിപത്യ'ത്തിന്റെ പ്രധാന പ്രത്യേകതയെന്താണ് ?
ഇന്ത്യന് ബ്യൂറോക്രസിയുടെ ഏറ്റവും ഉയര്ന്ന പദവികളിലേക്കുള്ള പരീക്ഷയായ സിവില് സര്വ്വീസ് പരീക്ഷയ്ക്കായി ഏഷ്യാനെറ്റ് ഓണ്ലൈനും അമൃത ഐഎഎസ് അക്കാദമിയും ചേര്ന്നൊരുക്കുന്ന ചോദ്യമാതൃകയുടെ നാല്പ്പത്തിയൊന്നാം ഭാഗം.
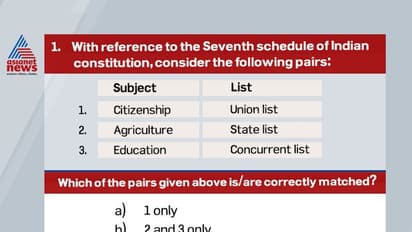
Answer (d)
Union List includes subjects like War and Peace, Naval, military and air force work, foreign jurisdiction, Citizenship, naturalization, and aliens. etc.
State List includes subjects like Agriculture, Police, Prison, Local Government, Public Health, Land, Liquor, etc.
Concurrent List includes subjects like Education, Transfer of Property other than Agricultural land, Forests, Trade Unions, etc.
Residuary Powers include all other matters not mentioned in any of the lists such as CyberSpace Union Legislature alone has the power to legislate on such matters.
Answer (b)
Statement 1 is incorrect. Representative democracy, also known as Indirect democracy, is in which the representatives elected by the people exercise the supreme power and thus carry on the government and make the laws. This type of democracy is of two kinds—parliamentary and presidential.
Statement 2 is correct. In a direct democracy, the people exercise their supreme power directly. There are four devices of direct democracy, namely-Referendum, Initiative, Recall, and Plebiscite. The recall is a method by means of which the voters can remove a representative or an officer before the expiry of his term when he fails to discharge his duties properly.
Answer (c)
Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania are the countries that open out to Lake Victoria.
Answer (b)
The Tropical Butterfly Conservatory Tiruchirappalli (TBCT) has been developed in Tamil Nadu’s Tiruchirappalli to create awareness among the public about the importance of the butterfly and its ecology.
It is located in the Upper Anaicut Reserve Forest, sandwiched between the Cauvery and Kollidam rivers in Tiruchirappalli.
It is spread over 27 acres and is considered to be Asia’s largest butterfly park.
Answer (d)
In 2016, MoFPI introduced an umbrella Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters or SAMPADA, which was later renamed as PradhanMantriKisanSampadayojana. It is a central sector scheme launched following objectives:
To Supplement Agriculture
To Create and improve processing and preservation capacities.
To Modernise food processing unit.
To add value to leading to reduction of wastage.
Components of the scheme
Mega Food Parks.
Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure.
Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Clusters.
Creation of Backward and Forward Linkages.
Creation/Expansion of Food Processing & Preservation Capacities.
Food Safety and Quality Assurance Infrastructure.
Human Resources and Institutions.
Answer (a)
Creative destruction can be described as the dismantling of long-standing practices in order to make way for innovation.
Creative destruction was first coined by Austrian economist Joseph Schumpeter in 1942.
Schumpeter describes creative destruction as innovations in the manufacturing process that increase productivity, but the term has been adopted for use in many other contexts.
Answer (b)
Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water between the Malay Peninsula and the Indonesian Island of Sumatra.
Answer (c)
The people of the Neolithic age lived in rectangular or circular houses which were made of mud and reeds. Neolithic men also knew how to make boats and could spin cotton, wool, and weave cloth.
With the advent of agriculture, people were required to store their food grains as well as to cook, eat the product, etc. That’s why it is said that pottery appeared in this phase on a large scale.
The people of the Neolithic age led a more settled life and paved the way for the beginning of civilization.
Answer (d)
G20: The G20 was formed in 1999, as a forum of Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors. India is a member of the G20 since it was established as Finance Ministers Forum in 1999.
IMF: India is a founder member of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) which was established to promote a cooperative and stable global monetary framework.
New Development Bank: BRICS Nations are the founding members of the New Development Bank (NDB), which has been instituted with a vision to support and foster infrastructure and sustainable development initiatives in emerging economies.
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB): India is one of the founding Members and the second-largest shareholder of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), a Multilateral Development Bank (MDB) set up in 2016.
Answer (b)
Vinaya Pitaka: It is a book of discipline. It deals with the monastic rules for monks and nuns. It is further divided into three books namely Suttavibhaṅga , Khandhakas, and Parivara.
Abhidhamma Pitaka: It comprises the philosophy and doctrine of Buddhism. It is divided into seven books namely Dhammasangani, Dhatukatha, Kathavatthu, Patthana, Puggalapannatui, Vibhanga, and Yamaka.
Jatakas: It comprises the stories of previous births of Buddha in the form of poems.
MilindaPanha: It contains the dialogue between Buddhist monk Nagasena and Indo-Greek king Meander.
Buddha Charita: It is written by Ashvaghosha in the Sanskrit language. It depicts primarily the life of Buddha.